Loving County to feds: Send us your nuclear waste — and $28 billion
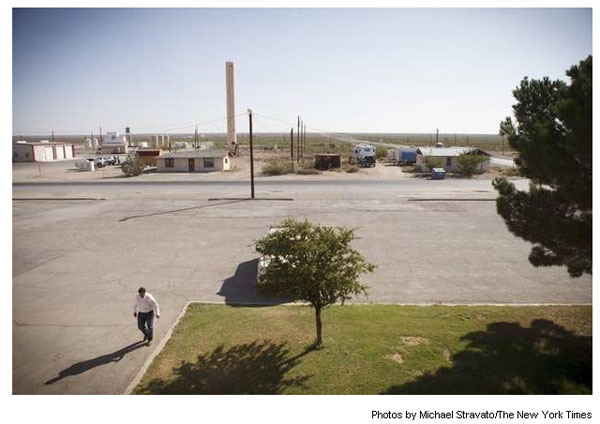

Skeet Jones, a Loving County judge, walks to the courthouse in Mentone. He backs locating a toxic waste storage facility in the county because of the money it would generate.
Published: 07 August 2014 08:01 PM
Updated: 07 August 2014 08:06 PM
Matthew L. Wald,
The New York Times
MENTONE — Loving County is big, dry and stretches for miles, and is the perfect place, local officials say, to store high-level radioactive waste.
Officials here hope to entice the federal government — with $28 billion to spend on the disposal of high-level radioactive waste — into considering the possibility.
"With the money that this would generate for the county, we might even be able to pay the taxpayers back," said the county judge, Skeet Jones. "We could build some roads. We could bring in some more water. We could have a town that’s incorporated, have a city council, maybe even start a school." Loving County had a school, but it has been boarded up for years, and students are bused to neighboring Winkler County.
"Maybe even have a Wal-Mart," Jones mused.
 About midway between El Paso and Midland-Odessa, Loving County, population 95, according to the Census Bureau, is spread across 650 square miles. Mentone, the county seat, has a courthouse, a single gas station, a food truck and not much else.
About midway between El Paso and Midland-Odessa, Loving County, population 95, according to the Census Bureau, is spread across 650 square miles. Mentone, the county seat, has a courthouse, a single gas station, a food truck and not much else.
"There are no lawyers, no bank, no hospital, no real estate agency, nothing," said Mozelle Carr, the county clerk. Carr is Jones’ sister.
The family, which makes up about a quarter of the voters in the county, is not unanimous in its support of a storage site. Their father, Elgin R. Jones, who goes by Punk and was sheriff from 1965 to 1992, said he foresaw trouble in anything radioactive. But he admits being in the minority.
The cancellation of the federal government’s plan to bury high-level radioactive waste at Yucca Mountain in Nevada means that the waste will remain at about 70 reactor sites around the country until there is some other plan. Loving County has visions of storing spent fuel from closed reactors in aboveground casks, and later, building a processing plant that would recover unused uranium, and plutonium for reuse, making the rest easier to bury. County officials are working with a company that is hoping to negotiate a deal with the state and federal governments. Two counties just across the state line in New Mexico are also seeking to become storage sites.
Any plan would probably require federal legislation, because the nuclear waste fund is supposed to be used for disposal, not storage. But Congress has an incentive; the Treasury is facing billions of dollars in damage claims because of the Energy Department’s delay.
Storing spent fuel in a central location, in preparation for burial or for reprocessing, looks more attractive as defunct reactors from Maine to California are torn down, and as reactor owners sue the Energy Department, which was supposed to begin accepting the waste for burial in 1998, to recover their costs.
"Interim" storage, though, would mean adding a cumbersome job: shipping the fuel a second time, for burial. Or maybe not. "If we let this waste into Texas, it’s likely never to be shipped anywhere else, because nobody really wants it," said Tom Smith, an energy advocate at Public Citizen in Austin.
Two lawyers in Austin, Monty G. Humble and Bill Jones, raised the idea with Gov. Rick Perry, who Humble said was "not opposed," and then went shopping for a county that would be interested. They argued that two counties in New Mexico, Eddy and Lea, were another possibility, and that if the waste were taken there that the New Mexico counties would get all the benefit but Loving would get some of the risk.
Humble, who specializes in energy topics, and Bill Jones, who was Perry’s first general counsel, formed a company, Advanced Fuel Cycle Initiatives, and have been negotiating with a landowner in the county. The county has designated the two as its agents in Austin, and the two are seeking the same designation from the state of Texas in order to negotiate with the Department of Energy over terms of a lease, including research grants to Texas universities, new roads and emergency equipment for towns in the area.
Perry has ordered a state study of the storage idea. "I believe it is time for Texas to act," he wrote in a letter in March, partly because New Mexico was considering a site within 50 miles of the Texas border.
While some Texas officials oppose the idea of a high-level storage site, some also see it as inevitable. "It’s going to be Texas," said Lon Burnam, a state representative from the Dallas area. "Everyone else is too smart to take it." Burnam fought hard against a low-level waste burial site, which is in Andrews, but was unsuccessful.
In Loving, Raymond Wildman, the cashier at Hopper Station, a gas station and convenience store that is also the county’s only retail outlet, offered another reason that could make a West Texas site attractive. Given the low population, he said, "We wouldn’t be missed if something happened."
This document contains copyrighted material whose use has not been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. SEED Coalition is making this article available in our efforts to advance understanding of ecological sustainability, human rights, economic democracy and social justice issues. We believe that this constitutes a "fair use" of the copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. If you wish to use this copyrighted material for purposes of your own that go beyond "fair use", you must obtain permission from the copyright owner.


